100 ECG’s
Conduction Defects: (17 questions)
Questions
-
1
73 year old man complains of chest pain while gardening. He has a past medical history of essential hypertension and smoking, but no family history of heart disease. He phones the ambulance which does an ECG on route to hospital. The student paramedic is challenged by the ECG findings and asks his senior for advice to make a decision on whether this patient should go for primary angioplasty or not. What is the most appropriate description for the ECG findings? 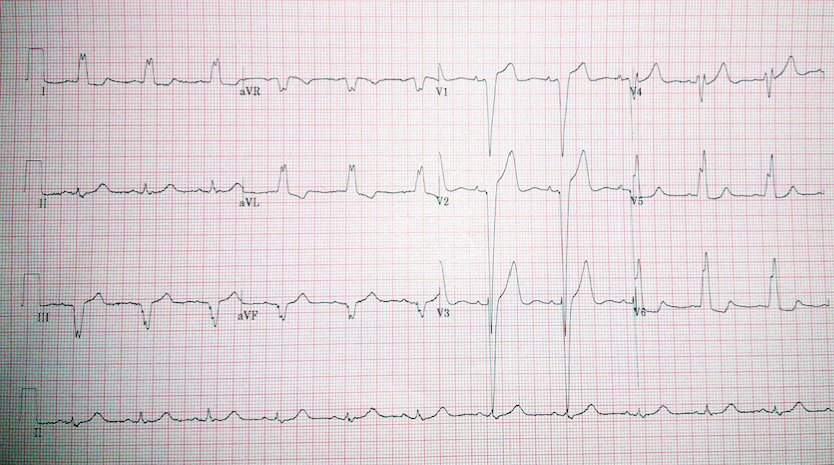
a Inferolateral ST-elevation b LVH and ST elevation in anterior leads c LBBB d Left Axis Deviation and LVH e Left Axis Deviation, LVH and LBBB -
2
A patient is admitted to the coronary care unit with troponin positive chest pain. His ECG is shown. What is the diagnosis ? 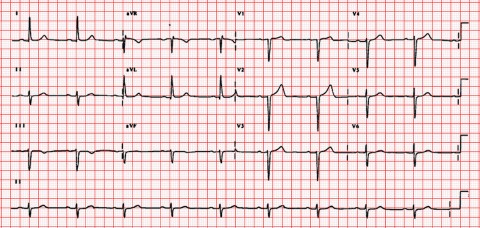
a Sinus rhythm with NSTEMI b First Degree Heart block with NSTEMI c Second degree heart block with NSTEMI d Complete heart block with NSTEMI e Left bundle branch block -
3
A 55 year old immigrant attends the GP clinic for a registration check-up. He has his ECG taken (shown). The GP is puzzled by the ECG. The pulse is irregular. The patient is asymptomatic. What is the best course of action? 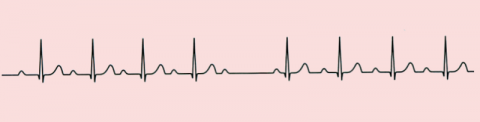
a Bisoprolol b Ivabradine c Permanent Pacemaker d Temporary pacing wire e Watch and wait -
4
A 45 year old man attends the GP new patient clinic. His cardiovascular examination is normal except for an irregular rhythm. The concerned GP performs an ECG (shown). The patient is asymptomatic. What is the best course of management? 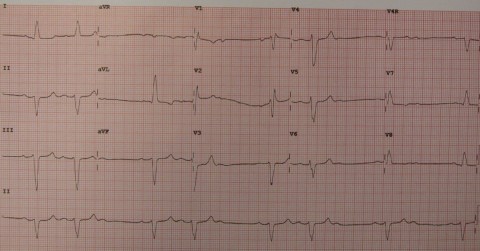
a Bisoprolol b Ivabradine c Permanent Pacemaker d Temporary pacing wire e Watch and wait -
5
While attending the cardiology outpatient clinic, a medical student stumbles across the ECG shown. What is the ECG pattern showing ? 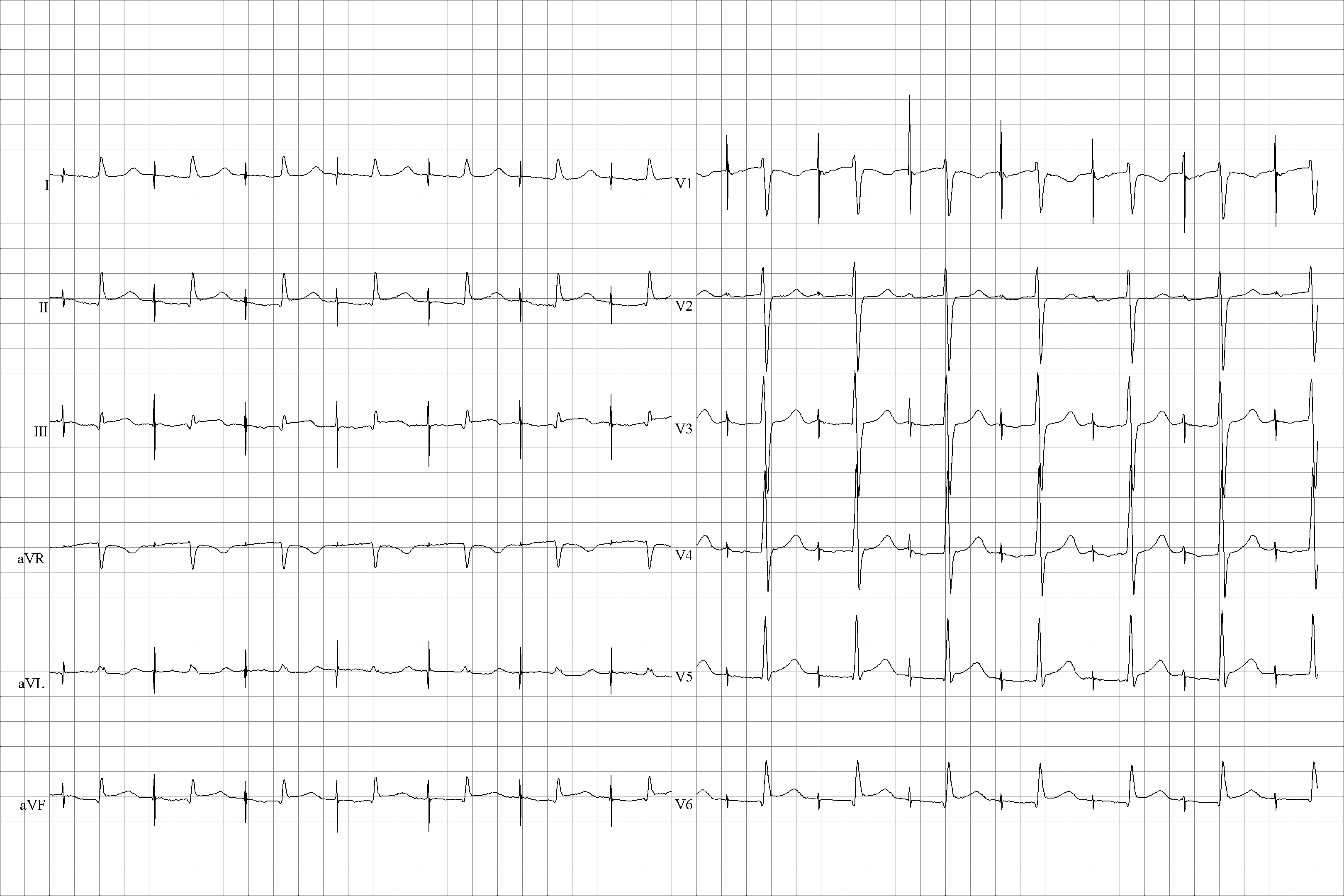
a Acute ST-Elevation MI b Atrial Pacing c Atrial Ectopics d Atrial Sensing e Ischaemic P-waves -
6
A medical student attends the end of year examination. He is asked to interpret the following ECG. The patient has a history of right coronary artery infarction 6 months ago. What does the ECG show? 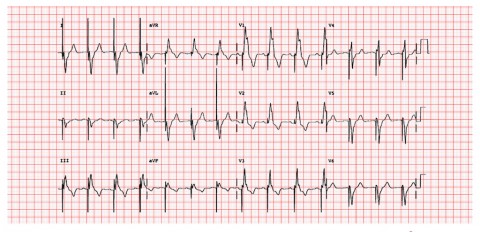
a Dual chamber pacing b Temporary pacing wire c NSTEMI d LBBB e RBBB -
7
24 hours after an inferior infarct, a patient develops a sudden reduction in the blood pressure and a collapse on the coronary care unit. His heart rate is noted to be 30bpm. His blood pressure is 80/38 and he is very short of breath. What is the best next step in the treatment of this patient ? 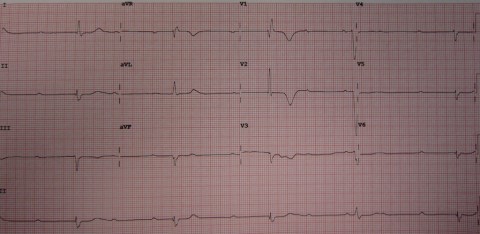
a Aspirin and Clopidogrel b Adenosine c Cardiopulmonary resuscitation d Transcutaneous pacing e Transvenous Pacemaker -
8
A 60 year old patient attends the emergency department with sudden onset central crushing chest pain of 45 minute duration. He has a history of hypertension and smoking. The triage nurse has doubts over the ECG as “it doesn’t seem to have a normal pattern”. You review the ECG (shown) and make which of the following decisions ? 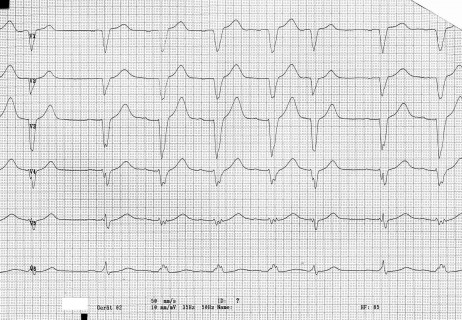
a Give IV Amiodarone b Send the patient for angioplasty c Send the patient home as his condition is benign d Start Cardiopulmonary resuscitation e Start heparin and fondaparinux -
9
As a medical student, you attend a teaching session with your cardiology consultant who has prepared an exciting case for you to discuss today. He starts off by handing you the following ECG and asks you to make a diagnosis. Which of the following is the diagnosis ? 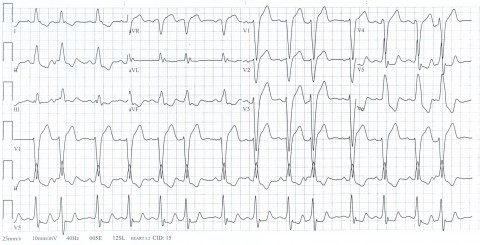
a First degree heart block b Left bundle branch block c Right bundle branch block d Trifascicular block e Dextrocardia -
10
During ward round, you see a patient 12 hours post admission to the coronary care unit with the following initial ECG and chest pain. He has had the appropriate treatment and is being monitored on the unit. As you are reviewing him, he develops severe shortness of breath, a pansystolic murmur at the apex and hypotension. What is the diagnosis ? 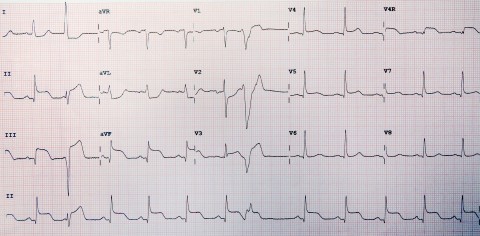
a Ventricular septal rupture b Papillary muscle rupture c Free ventricular wall rupture d First degree heart block e Cardiac tamponade -
11
A sixty-two year old patient 48 hours after being admitted with a NSTEMI has a routine in patient ECG. He is asymptomatic and pain-free and is due to be discharged tomorrow. His ECG (partial) is shown. What is the best course of management ? 
a Permanent pacemaker b Temporary pacing wire c cardiac resynchronisation therapy (CRT) d Do Nothing e AV node ablation -
12
24 hours after an inferior infarct, a patient develops a sudden reduction in the blood pressure and a collapse on the coronary care unit. His heart rate is noted to be 30bpm. His blood pressure is 80/38 and he is very short of breath. What is the most appropriate long-term treatment ? 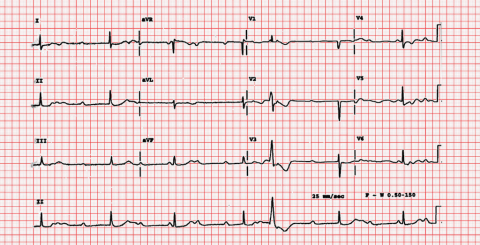
a Aspirin and Clopidogrel b Atropine c Cardiopulmonary resuscitation d Transcutaneous pacing e Permanent Pacemaker -
13
During the 8am ward round with your consultant, you review a patient 14 hours post admission to the coronary care unit with the following initial ECG and chest pain. During your review, the patient develops severe shortness of breath, a pansystolic murmur at the left lower sternal edge and hypotension. What is the diagnosis ? 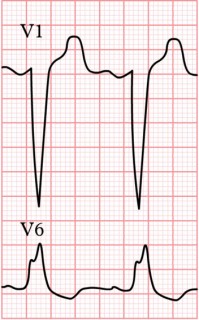
a Ventricular septal rupture b Papillary muscle rupture c Free ventricular wall rupture d First degree heart block e Cardiac tamponade -
14
A 51 year old lady is being assessed at the pre-op clinic for an upcoming hysterectomy. She is a non-smoker, with no past medical history except for peri-menopausal bleeding. She takes norethisterone and tranexamic acid. A routine ECG is performed (shown). What is the most likely diagnosis ? 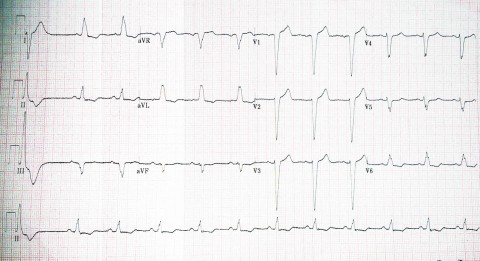
a Right bundle branch block b Left bundle branch block c Hyperkalaemia d Rate-controlled Ventricular tachycardia e Atrial fibrillation with right bundle branch block -
15
A new patient is being assessed in the emergency department for chest pain. The doctor reviews the patient who complains of central chest pain, tender chest wall, and pain that increases on inspiration. The doctor asks a medical student to perform base line investigations including observations and an ECG. The medical student runs back to the doctor with an ECG and is worried about anterior ST elevations. What is the likely diagnosis ? 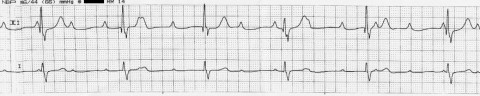
a Dual chamber pacing b ST-elevation MI c Non-ST-elevation MI d LBBB e RBBB -
16
As you are approaching your final exams, you are revising the different types of cardiac arrhythmias when you stumble upon this ECG (shown). What type of arrhythmia is this? 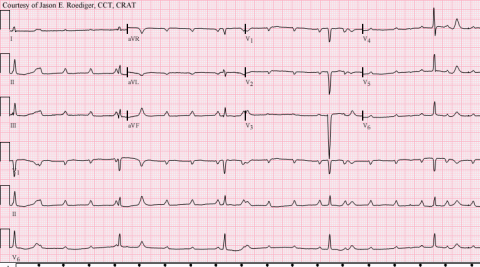
a First degree heart block b Second degree heart block (Mobitz I) c Second degree heart block (Mobitz II) d Third Degree heart block e Trifascicular block -
17
You are revising for your finals and you bump into a strange ECG on one of your lecture slides with no annotations (shown). You attempt to interpret it. What are the abnormalities in this ECG ? 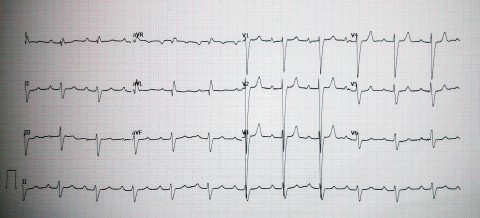
a Right bundle branch block b First Degree Heart block with NSTEMI c Second degree heart block with left bundle branch block d First degree heart block with left bundle branch block e Paced rhythm