100 ECG’s
Electrolyte Disorders: (4 questions)
Questions
-
1
A 60 year old gentleman with a long standing history of chronic kidney disease due to diabetes attends the emergency department. He is on the right mixture of medications, including lisinopril, insulin and atorvastatin. He says he has recently felt very drowsy and weak. The ECG is shown. What is the best initial course of action ? 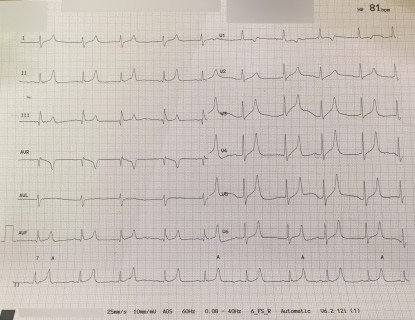
a Nebulised Salbutamol b IV calcium gluconate c IV salbutamol d IV insulin and dextrose e IV bicarbonate -
2
A 57 year old gentleman with end-stage renal failure is admitted to the emergency department with drowsiness and confusion. On examination, he has a dialysis fistula in his left arm, a rapid respiratory rate, and decreased deep tendon reflexes. You perform an ECG (shown) followed by an arterial blood gas. What is the most likely acid-base status in this patient ? 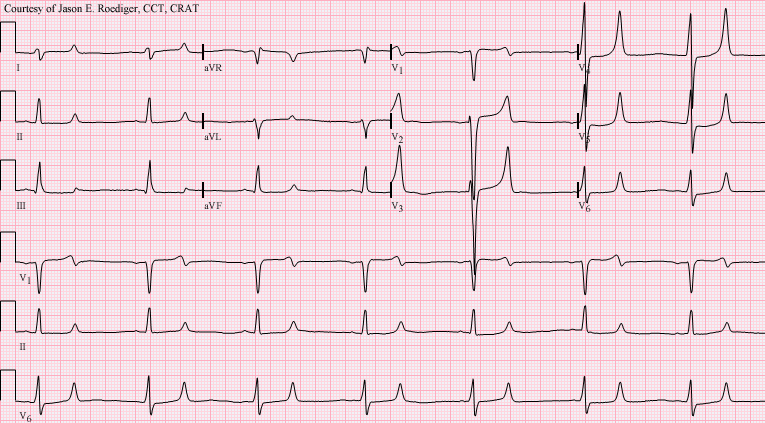
a Metabolic Acidosis b Metabolic Alkalosis c Normal d Respiratory Acidosis e Respiratory Alkalosis -
3
A 52 year old man with longstanding heart failure develops severe viral gastroenteritis and vomiting. He has vomited up to ten times a day and has become very drowsy. His wife accompanies him but doesn’t remember his complete past medical or drug histories, although she does recall him being on a “water tablet”. An ECG is performed (shown). What is the most likely diagnosis? 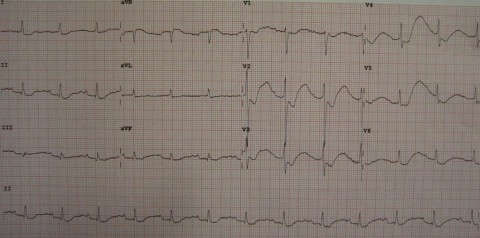
a Hypercalcaemia b Hypocalcaemia c Hyperkalaemia d Hypokalaemia e Hypomagnesemia -
4
You are called to a cardiac arrest situation during one of your night shifts. You arrive and resuscitation is ongoing. You are handed an ECG (shown) and asked to identify any reversible causes which can be addressed in this patient. Which of the following is a reversible cardiac arrest cause in this patient ? 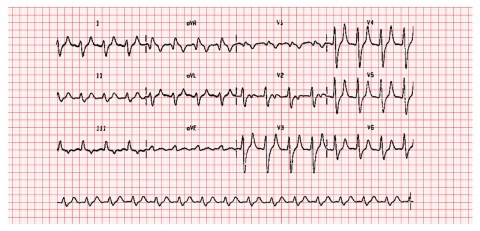
a Hypothermia b Hyperkalaemia c Hypokalaemia d Cardiac tamponade e Pulmonary embolus (right heart strain)